Broca’s Area And Language Production

Language production is the ability of humans to communicate through a symbolic system called language. This ability has helped us a lot throughout our evolutionary history. The ability to communicate effectively has allowed us to collaborate and create complex societies to face a hostile world. This is the reason why we find biologically rooted nuclei such as Broca’s area in the brain.
An essential aspect of the neural disposition of language is that it is lateralized. In other words, the vast majority of structures related to language are found in the left hemisphere; It is true that there are studies which claim that processes such as jokes, pragmatics and sarcasm are handled in the right hemisphere. The Broca area, responsible for the production of the tongue, is located in the left hemisphere, in particular in area 44, according to Brodmann areas.
In this article, we will deal with two fundamental aspects to understand the implication of Broca’s area in language. The first will be its anatomical and functional aspects. And the second will relate to Broca’s aphasia, generated by lesions in this area.
Anatomy and functionality of Broca’s area
We have discovered over time that Broca’s area is not the only one involved in language production. Apart from Brodmann area 44, areas 45, 47 and a large part of area 6, are also. Therefore, it would be more correct to speak of the Broca system, encompassing all the areas responsible for the production of the language.
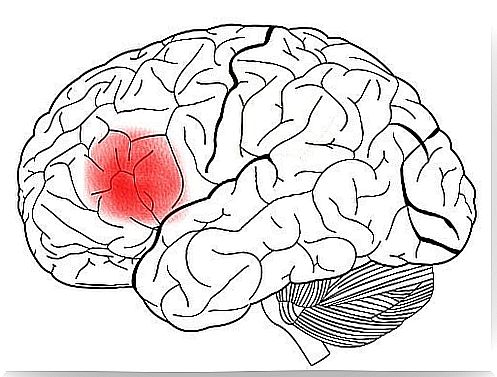
We can find a subdivision into two large structures within the Broca system itself: (a) the triangular and (b) the opercular. The triangular area would be located in the anterior part to Broca’s area, while the opercularis would be located in the posterior part. At the anatomical level, it is also relevant to talk about the major connections that this system has with Wernicke’s area; this area is mainly responsible for understanding the language. These two areas (Wernicke and Broca) are connected by a series of neural bundles, which in turn form what we call the arched fascicle.
The functions performed by the Broca area are as follows:
- Production of verbal behavior, both in spoken and written form.
- Management of graphemes, phonemes and words to structure grammar and morphology.
- Coordination of the articulatory organs to regulate the pronunciation of the tongue.
- Regulation of prosody, tone of voice and rhythm of speech.
These functions are the pillars that support adequate language production, enabling communication. Therefore, lesions in Broca’s area can have significant negative consequences during the use of language and communication. In the next section, we will discuss the specific consequences of lesions in the said area.
Broca’s aphasia
Broca’s aphasia is a speech production disorder caused by lesions in Broca’s area. This disorder is characterized by slow speaking, performed with effort and in a non-fluid manner. But, although the pronunciation is often disturbing, the message conveyed is generally significant, leading us to conclude that the semantics are not damaged in this type of disorder.

Some words are easier for people with Broca’s aphasia to pronounce than others. For example, functional words (one, the, on, of…) are much more difficult for patients to pronounce than content words. This is mainly due to the fact that the former are words of grammatical use only and that the management of the grammar is the responsibility of the Broca area. On the other hand, since the semantics remain intact, the content words are easier to pronounce.
Another fundamental aspect of Broca’s aphasia is that the understanding of the language also remains intact. People with this disorder have no problem reading or listening to the language. This is so because the structure of the brain responsible for this process is the Wernicke area. This helps us to understand that Broca’s area is specialized in language production and, despite its links with other domains, these domains remain able to continue to function independently.
Finally, a curious process is that which occurs when a lesion appears in areas of speech at a very young age. Due to the great plasticity of the brain, if the left hemisphere is damaged, it is possible for language to develop in the right hemisphere. As a result, brain damage before speech consolidation can be reduced, thus achieving normal or near normal development.